Triphenyl phosphate CAS 115-86-6 TPP
Triphenyl phosphate CAS 115-86-6 TPP
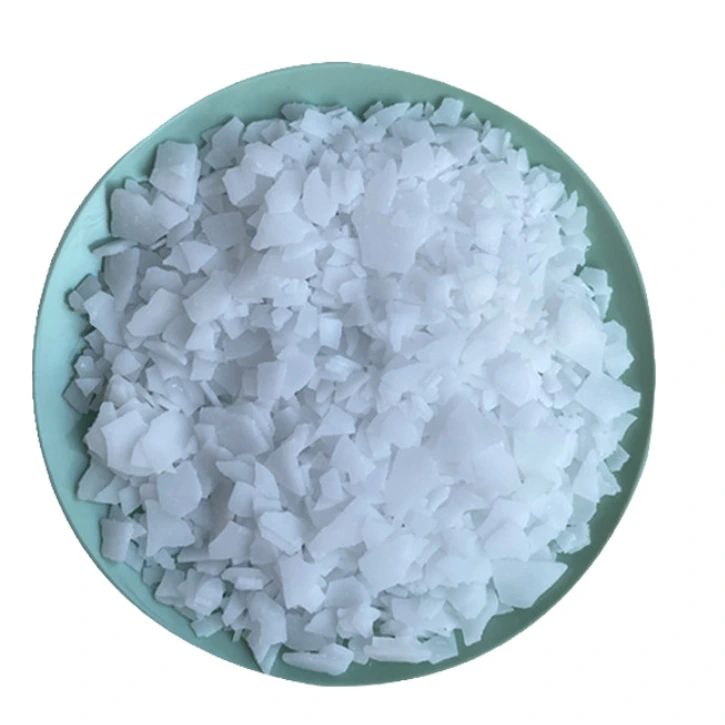
Triphenyl phosphate, TPP, CAS 115-86-6, is mainly used for the flame retardancy of cellulosic resins, vinyl resins, natural rubber and synthetic rubber.
Product Details
| Purity | ≥99% |
| Acid Value (mgKOH/g) | ≤0.07 |
| Density (50ºC) | 1.185-1.202 |
| Freezing Point | ≥48.0ºC |
| Color (APHA) | ≤50 |
| Moisture | ≤0.1% |
Uses: It is mainly used as a flame-retardant plasticizer for engineering plastics and phenolic resin laminates; as a softener for synthetic rubber and a raw material for the production of trimethyl phosphate, among other applications; and as a flame-retardant plasticizer, flame-resistant solvent for nitrocellulose and cellulose acetate, nitrocellulose lacquers, synthetic resins, an impregnating agent for roof paper, and a camphor substitute in celluloid manufacturing, etc.
FAQ
The target market of our brand has been continuously developed over the years. For more information, please reach our team, we are more than happy to help.
With a professional and experienced team, coupled with strong technical support from our partnerships with research institutes, we excel in developing innovative chemical products for our customers. If you are seeking to source new products, we are undoubtedly your ideal choice.